A year ago, most business owners were still asking if AI search would ever matter for their marketing. That question has been answered. Between January and May 2025, AI-referred sessions jumped 527% across 19 GA4 properties. Some SaaS sites now see more than one percent of all visits starting inside AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Claude, and Copilot.
What’s more surprising is how these visits happen. A buyer can ask an AI chatbot a question, read the answer, remember your brand, and come to you later without ever clicking a link in Google Search. Semrush research now predicts LLM traffic will overtake Google Search by 2027. Nearly 90% of ChatGPT’s citations come from content that doesn’t even sit in the top five results of traditional search engines.
That’s why SEO for LLM has become less about fighting for position one and more about being the trusted answer AI systems choose. It’s about creating content with direct answers, structured data, relevant entities, and clear user intent in mind. Generative engine optimization is the approach that makes your brand visible in this new discovery layer.
In this Guide:
- What is LLM in SEO?
- From Traditional SEO to LLM Optimization (What Actually Changes)
- Practical Checklist: Optimizing Content for LLM Selection
- Authority Signals That Influence LLM Selection
- Structuring Content So LLMs Can Read It
- Content Formats LLMs Prefer to Cite
- Building Topic Clusters for LLM Optimization
- Optimizing for Conversational and Natural Language Queries
- Integrating Relevant Entities into Your Content
- Leveraging Multi-Platform Visibility for AI Search
- Future Trends in LLM SEO and Generative Engine Optimization
What is LLM in SEO?
A large language model (LLMs) is an AI system trained on massive amounts of text and code to understand and generate human-like responses. These models process natural language queries, search training data or live web content, and deliver direct answers.
LLM optimization means creating content that these AI systems can easily find, interpret, and trust enough to feature in their responses. Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on rankings, LLM SEO is about being selected as a reliable source when AI delivers an answer. And most of the time, it’s before a user ever visits your site.
From Traditional SEO to LLM Optimization (What Actually Changes)
Search engines no longer reward visibility the same way. Traditional SEO performance depends on search rankings, keyword density, and exact keyword matches. Large language model optimization changes the focus to how AI models process user queries, evaluate brand mentions, and select answers.
LLMs prefer content that meets clear user intent, uses conversational keywords, and delivers structured context that works in AI-driven search. Measuring success goes beyond Google rankings or search volume. It includes LLM visibility, search referrals, and how often your brand appears in LLM responses, which helps build brand presence and recognition.
How Large Language Models Process and Select Content
When a user enters a query, many AI models break it into smaller, related questions. They search training data and live web sources to find the most relevant chunks of information. Content appears in LLM responses when it matches the context, offers clarity, and aligns with user intent.
LLMs prefer content that is well-structured, easy to parse, and backed by credible brand mentions. Factors like topic depth, entity alignment with Google’s Knowledge Graph, and recent updates can influence selection and boost the brand’s visibility.
Key Differences Between Traditional SEO and LLM Optimization
Traditional SEO focuses on improving search rankings within search engine results. The main levers are keyword targeting, backlinks, and on-page optimization. The assumption is that higher positions bring more clicks. Metrics like Google rankings, search volume, and organic search traffic dominate reporting in Google Analytics.
LLM optimization works differently. The priority is to become a trusted source in AI-driven search. LLMs look beyond ranking position and evaluate whether the content answers the question, fits within the context, and supports the credibility of the brand.
In LLM optimization, brand mentions across authoritative sites, alignment with relevant entities in Google’s Knowledge Graph, and conversational keywords become strong signals. Even if content ranks lower in traditional search, it can appear in LLM responses if it offers a unique perspective or up-to-date information.
Traditional SEO performance is often tied to click-through rate. LLM visibility is measured by how often the brand appears in AI answers and the resulting brand recognition from AI search referrals. This shift changes how content teams optimize and how performance is reported. The goal is no longer only about ranking higher but about becoming the content LLMs choose to surface.
Aspect | Traditional SEO | LLM Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Rank high in search engine results | Appear in LLM responses |
| Key Metrics | Google rankings, search volume, organic clicks | LLM visibility, brand mentions, AI search referrals |
| Content Focus | Keyword targeting, on-page SEO | User intent, structured content, conversational keywords |
| Authority Signals | Backlinks from high DA sites | Brand mentions, entity alignment, credible sources |
| User Journey | Search → Click → Visit site | AI answer → Brand awareness → Direct visit |
| Algorithm Type | Search algorithms prioritize ranking signals | LLMs select content based on relevance and clarity |
| Impact of Ranking Position | Critical to traffic | Less critical if content answers well |
| Optimization Scope | SERP-focused | Multi-platform AI models including Google Gemini, ChatGPT, Perplexity |
The New KPIs for LLM Optimization
In LLM optimization, clicks and ranking position tell only part of the story. AI-generated answers can shape user decisions long before they reach your site. Someone may encounter your brand in a response, recall it later, and visit directly or search for it by name. Analytics will register this as direct traffic or a branded search, masking the AI’s role in the journey.
How to Track LLM Search Visibility
- AI Visibility Tools: Platforms like Semrush’s AI Toolkit and Similarweb’s AI search modules monitor brand mentions in AI answers, citation frequency, and share of visibility against competitors.
- Branded Search Tracking: Use Google Search Console to monitor changes in branded queries and correlate spikes with known AI answer appearances.
- Content Coverage Audits: Track whether your core topics and entities are well represented in authoritative sources that AI models prefer to cite.
- Direct Traffic Trends: Annotate content that has been cited in AI results and watch for correlated increases in direct visits in Google Analytics.
- Sentiment and Mention Analysis: Tools like Brandwatch or Mentionlytics can help gauge sentiment and context when your brand appears in public datasets AI systems may pull from.
Practical Checklist: Optimizing Content for LLM Selection
- Map Natural Language Queries
- Identify how your audience phrases questions in conversational form.
- Use data from Google Search Console, People Also Ask, and community forums.
- Front-Load Direct Answers
- Place a concise, factually correct answer in the opening lines of each section.
- Expand with context and examples further down.
- Use Structured Formatting
- Apply clear H1/H2/H3 headings and semantic HTML.
- Break content into short paragraphs and scannable bullet points.
- Integrate Relevant Entities
- Reference people, places, products, or concepts tied to your topic.
- Align with entries in Google’s Knowledge Graph where possible.
- Build Authority Beyond Links
- Secure brand mentions in industry publications and trusted directories.
- Maintain consistent topical coverage across your site.
- Maintain Freshness
- Update high-value pages with current information.
- Add new examples, data, or case studies regularly.
- Strengthen Internal Linking
- Connect related articles with descriptive anchor text.
- Create topic clusters that demonstrate depth.
- Track LLM Visibility
- Monitor brand mentions and citation frequency using AI visibility tools.
- Correlate LLM appearances with branded search and direct traffic trends.
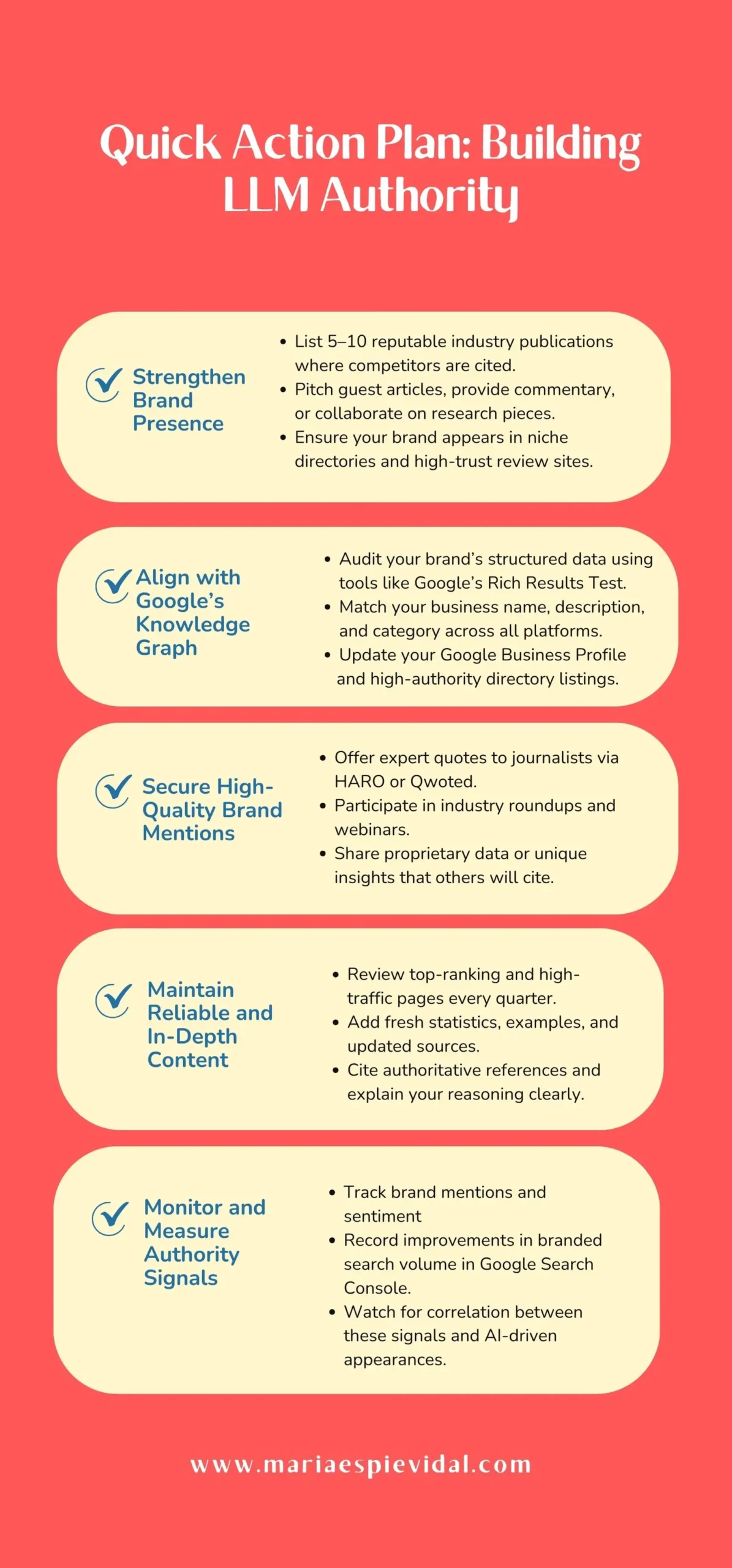
Authority Signals That Influence LLM Selection
Large Language Models weigh credibility differently from traditional search engines. While backlinks and ranking position still contribute to trust, they are only part of the picture. LLMs prefer content that demonstrates authority across multiple touchpoints, from brand mentions in respected publications to accurate entity data that matches Google’s Knowledge Graph.
Consistent Brand Presence Across Reputable Sources
Authority starts with being visible where trust already exists. When your brand appears in respected industry publications, niche directories, or well-known review sites, it sends strong credibility signals to LLMs. These mentions help the model verify your relevance within a specific topic or sector.
To strengthen brand presence, target publications that your competitors are cited in, contribute thought leadership articles, and engage in interviews with industry media. This strategy creates a web of references that AI systems can find, cross-check, and include in responses.
Entity Alignment with Google’s Knowledge Graph
LLMs use Google’s Knowledge Graph and similar databases to confirm facts about your brand, such as your services, location, and industry connections. If this information is missing or inconsistent, your credibility score drops.
Audit your entity data across all major platforms, including your website schema markup, Google Business Profile, and high-authority directories. Ensure your brand name, description, and category match across these sources. Add structured data for articles, products, and reviews where relevant.
The Value of Brand Mentions Without Links
Being named in content can be just as powerful as earning a backlink. A brand mention on a credible site shows that your expertise is recognized in the wider conversation. LLMs collect and evaluate these mentions when deciding whose content to select.
Proactively seek mentions by contributing quotes to journalists, participating in expert roundups, and sharing data or insights others can reference. Monitor your mentions using tools like Brandwatch or Mentionlytics to track growth and sentiment.
Content Reliability and Depth
LLMs prefer content that can be trusted to provide accurate and complete answers. This means factual correctness, regular updates, and clear coverage of the topic. Thin content, outdated statistics, or vague claims lower the chances of selection.
To boost reliability, include original research, cite authoritative sources, and clarify your reasoning where appropriate. Review and refresh your top-performing pages regularly, adding new data, examples, and relevant insights.
Structuring Content So LLMs Can Read It
Even the most insightful content can be overlooked if LLMs can’t easily process it. These models scan text for clarity, logical flow, and identifiable structure before deciding whether to include it in a response.
Proper formatting and semantic organization not only improve human readability but also increase the likelihood your content will be recognized, understood, and cited by AI systems. Structuring for LLMs means thinking about how the model parses headings, answers, and supporting details.
Build a Clear Heading Hierarchy
LLMs use headings as signposts to navigate your content. A logical hierarchy—H1 for the main topic, H2 for primary sections, and H3 for supporting points—helps the model map your information. Avoid vague headings; instead, turn them into specific, answer-focused statements.
For example, “Benefits of Structured Data for LLM SEO” is more useful than “Why It Matters.” This approach makes it easier for AI systems to match user queries to the right section of your page.
Place Direct Answers Up Front
When answering a question, start with the most direct, factually correct response in the opening lines. Then follow with supporting context, examples, and related insights. This mirrors how featured snippets work in traditional search and helps LLMs extract concise, relevant text. Users scanning AI-generated answers are more likely to remember a brand that delivers a clear, immediate solution.
Use Semantic HTML and Structured Data
Beyond visible headings, semantic HTML tags such as <section>, <article>, and <aside> provide extra cues about the role of different content blocks. Pairing this with structured data like FAQPage, HowTo, or Product schema gives LLMs an explicit framework for interpreting your content. Test your markup in Google’s Rich Results Test to confirm accuracy and compatibility.
Keep Paragraphs Token-Friendly
LLMs process content in “tokens,” which are chunks of text. Overly long paragraphs risk being truncated or skipped. Keep paragraphs short—three to five sentences—and break complex topics into smaller sections. This not only improves readability but also ensures more of your content fits within the model’s processing window.
Summarize with Takeaway Sections
Conclude each major section with a short, self-contained summary. Label it clearly as a “Key Takeaway” or “Summary” block. LLMs often lift these summaries into responses because they are concise, stand-alone, and easy to attribute. Include your brand name naturally in these takeaways to reinforce recognition.
Content Formats LLMs Prefer to Cite
LLMs do not favor content based on length or keyword count alone. They select sources that match the user’s intent, provide clarity, and present information in a format that is easy to extract and verify. Certain formats give your content a better chance of appearing in responses because they naturally align with how AI models parse and summarize information.
Long-Form, Topic-Focused Articles
Well-researched, in-depth articles remain a strong foundation for LLM optimization. These pieces allow you to cover a topic comprehensively, addressing related sub-questions that an AI model might generate during query fan-out. Breaking the content into clear sections with direct answers ensures each part can be cited independently. Unlike thin or overly general posts, long-form content provides the depth and authority LLMs seek when deciding whose information to include.
FAQs and Question-Led Sections
LLMs often respond to conversational queries that mirror FAQ-style questions. Having a dedicated FAQ page or question-based subheadings within articles increases the chances of matching the exact phrasing or intent of a user query. Each answer should be concise, factual, and able to stand alone without additional context. This structure makes it easier for the model to extract and cite your response verbatim.
Data Tables, Lists, and Comparisons
Structured formats like tables, bullet lists, and comparison charts make information easy for LLMs to parse. A table showing feature-by-feature comparisons or a list outlining step-by-step instructions allows AI systems to lift relevant portions without misinterpreting the content. These formats also help with retrieval augmented generation, where models pull small, high-value content chunks to build an answer.
Transcribed Video and Audio Content
LLMs can access and interpret transcripts from video and audio content. Publishing transcripts for webinars, podcasts, or product demos gives your multimedia assets the same visibility potential as written content. Transcripts should be cleaned for clarity and organized with timestamps or thematic headings so the model can match segments to relevant user queries. This not only broadens your reach but also increases topical authority across different media types.
Building Topic Clusters for LLM Optimization
Large Language Models analyze not only the depth of an individual page but also the breadth of your coverage on related queries. When your content forms a connected network—covering the main topic, its subtopics, and related user questions—LLMs can more easily identify your brand as a reliable source for multiple query variations.
Defining the Core Topic and Pillar Page
Your core topic is the foundation of a topic cluster. It defines what your brand should be known for and gives LLMs a clear context for your expertise. The pillar page will act as the authoritative hub connecting all related subtopics.
- Choose a Core Topic with Depth
Identify a broad subject that relates to your offerings but is focused enough to show expertise. Check that it has enough related subtopics to justify a cluster. - Validate with User Intent and Query Variety
Use keyword tools, People Also Ask, and AI prompt tests to confirm the topic matches multiple natural language queries. - Map Out Subtopics
List at least 5–10 related questions or angles. Each will become its own supporting content page. - Plan the Pillar Structure
Create an outline where the pillar page gives an overview and links directly to each subtopic page. - Write for Humans and LLMs
Use clear headings, concise explanations, and context that ties all subtopics together so both readers and AI systems can navigate easily.
Creating Supporting Content for Comprehensive Coverage
Supporting content, or “spoke” pages, builds depth around your pillar topic. Each page targets a specific subtopic, providing enough detail and context for LLMs to cite it independently in responses.
- Assign One Subtopic per Page
Avoid combining multiple subtopics on a single page. Give each a dedicated URL so LLMs can clearly associate it with a specific query. - Answer the Query Directly
Start each page with a concise, accurate answer to the subtopic’s main question. Follow with expanded details, examples, or data. - Add Contextual Links
Link back to the pillar page and to other relevant spoke pages. This strengthens topical relationships in the eyes of LLMs and search engines. - Incorporate Relevant Entities
Include people, products, or concepts tied to the subtopic, and align them with recognized entities in Google’s Knowledge Graph. - Update Regularly
Refresh statistics, examples, and references to keep the page current. LLMs prefer content that reflects up-to-date, reliable information.
Internal Linking to Strengthen the Cluster
Internal linking is what binds a topic cluster together and signals to both search engines and LLMs that your content is interconnected. Every spoke page should link back to the pillar page using descriptive anchor text that matches the subtopic’s context.
Linking between related spoke pages is just as important. If two subtopics overlap, such as “email segmentation techniques” and “personalizing email campaigns,” connecting them helps LLMs understand that your coverage extends beyond isolated articles. This creates a web of relevance where any page in the cluster can pass authority and context to others.
Consistency matters here. Use a logical, repeatable linking structure so new content can be added without breaking the pattern.
Optimizing for Conversational and Natural Language Queries
LLMs respond best to content that reflects how people naturally ask questions. Matching this style increases the chances your page is selected for AI-generated answers.
- Research Real Questions
Use Google’s People Also Ask, Reddit threads, Quora, and customer support logs to find authentic user phrasing. - Mirror Natural Language
Write headings and opening lines using the same structure people use in queries, including full questions. - Cover Context, Not Just Keywords
Go beyond inserting terms. Provide background, examples, and related details that help an AI deliver a complete answer. - Include Variations
Work in synonyms, alternative phrasings, and regional language differences so the content can match multiple query styles. - Place Answers Up Front
Start sections with a clear, concise response before expanding into explanations. - Blend Long-Tail Keywords with Intent
Target specific phrases that reveal a problem, decision point, or goal, making it easier for LLMs to connect your content to relevant prompts. - Test with AI Tools
Enter sample queries into LLM-powered search interfaces to see how your content matches and refine based on the results.
Integrating Relevant Entities into Your Content
Entities are the people, places, products, concepts, and organizations that search engines and LLMs use to understand content context. This goes beyond keyword use. It’s about linking your content to recognized, authoritative references that strengthen meaning and credibility.
Identifying the Most Relevant Entities for Your Topic
The first step to leveraging entities is knowing which ones matter most to your audience and to LLMs processing your content. Start by reviewing your target topic and mapping out related people, brands, organizations, locations, and concepts that are widely recognized in your industry.
You can find these entities by analyzing top-ranking content, exploring Wikipedia entries, checking Google’s Knowledge Graph panels, and reviewing structured data in competitor pages. Tools like Google Search Console’s performance report can reveal which entity-related queries already drive traffic to your site.
Focus on entities that have direct relevance to your main topic and strong connections to related queries. For example, if your content covers “local SEO strategies,” relevant entities might include Google Business Profile, Yelp, Bing Places, and location-specific terms tied to your target market.
Adding Entities Naturally into Your Content
Start by placing them in key on-page elements—headings, opening paragraphs, and image alt text—where they contribute to context without disrupting the flow.
Mention entities in ways that feel organic to the topic. For example, instead of stuffing “Google Business Profile” into every sentence, use it where it makes sense: when explaining local listing optimization or describing how search engines validate business information.
Supporting entities with relevant details also helps. Pair the name with related statistics, examples, or use cases to provide LLMs with more context for interpretation. This signals not only that the entity is relevant, but also that your page is authoritative on the subject.
Embedding entities in structured data, such as schema markup, further strengthens these connections. Search engines and LLMs read this information to verify relationships between entities, topics, and your brand.
Connecting Entities to Authoritative Sources
Referencing authoritative sources strengthens the credibility of your entities and helps LLMs confirm their relevance. Link to a reputable site that provides accurate and well-established information. This could be an official brand website, a trusted industry publication, or a respected database like Wikipedia.
These outbound links act as verification points, signaling to search engines and AI systems that your content is grounded in credible references. For example, if you mention “Google Analytics,” linking to Google’s official documentation reinforces the association between your content and the verified entity.
Consistency across your site also matters. When you reference the same entity in multiple articles, maintain the same linking approach.
Tracking Entity Performance
Measuring the impact of entity integration helps you refine your approach and identify which ones drive the most visibility. Start by monitoring impressions and clicks in Google Search Console for queries related to your targeted entities. Look for patterns showing increased exposure after adding or improving entity mentions.
Google Analytics can also reveal whether traffic from entity-related searches converts or engages more deeply with your content. If you’re using schema markup, structured data testing tools, and Rich Results reports can confirm whether search engines are correctly recognizing your entity connections.
Third-party platforms that track Knowledge Graph appearances or entity-based rankings can give deeper insight into how often your content is linked to specific entities in AI-generated answers.
Leveraging Multi-Platform Visibility for AI Search
AI-driven search is not limited to Google. LLMs draw answers from a wide range of platforms, knowledge bases, and content sources. This means your visibility across multiple platforms—such as industry publications, authoritative blogs, video platforms, and Q&A communities—can influence whether your brand appears in AI responses. The goal is to create consistent, high-quality signals across channels so your expertise is recognized no matter where the query originates.
Prioritizing Platforms That Feed LLMs
Not every platform has the same influence on LLM-generated answers. Some are more likely to be crawled, referenced, and trusted as sources.
High-Priority Platforms:
- Wikipedia and Wikidata – Frequently referenced by LLMs for entity definitions and background information.
- Authoritative Industry Publications – Well-known news outlets and niche authority sites in your field.
- Official Brand Websites – Verified and up-to-date pages for products, services, and corporate information.
- Google Business Profile – Critical for local and branded queries.
- YouTube – Indexed for video-based responses and how-to content.
- GitHub or Technical Documentation Hubs – Essential for technical or developer-focused content.
- Trusted Q&A Communities – Sites like Stack Overflow or Quora for problem-solving and knowledge-sharing.
Future Trends in LLM SEO and Generative Engine Optimization
The landscape of search is shifting dramatically. Traditional SEO is evolving into strategies that cater to AI-powered platforms and LLM-driven search. Under this new paradigm—often called Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), Answer Engine Optimization (AEO), or Artificial Intelligence SEO—key success factors include structured, easily extractable content, entity alignment, and fast-loading, machine-optimized pages.
GEO — SEO for the AI-First World
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) focuses on making your content easily citable and digestible by AI systems. Instead of ranking tweaks, GEO prioritizes structured, concise formats—like bullet points, comparison tables, and short answer blocks—that LLMs can quickly incorporate into responses. It’s about designing content that AI can slice, reference, and synthesize.
The Rise of AEO — Optimizing for Conversational Answers
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) centers on crafting content that delivers precise, conversationally phrased answers. As users increasingly rely on tools like Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, or Perplexity, businesses are adapting by structuring answers to match natural speech patterns and common user questions. This shift is gaining speed, especially as more brands move away from click-driven strategies.
Zero-Click and AI Overviews Dominate Results
AI-generated snippets are replacing traditional search results. Zero-click experiences—where users get answers directly from AI without clicking any links—now account for a large share of search interactions. In fact, interest in “AI overview” has surged dramatically, by about 99x in recent years. Only a small fraction of users proceed to click traditional links.
User Behavior and Interface Shifts Reshape SEO
AI isn’t just changing content strategies—it’s changing how users search. Around 80% of consumers now complete approximately 40% of their searches without ever clicking links. Meanwhile, generative models are guiding not only discovery but also commerce, pushing marketers to rethink content, tech infrastructure, and UX.
Make Your SEO for LLM Strategy Work for You
LLM optimization is no longer optional—it’s becoming the new standard for staying visible as AI-driven search reshapes how users find and interact with brands. From building topic clusters and optimizing for conversational queries to integrating relevant entities and expanding multi-platform visibility, the brands that act now will have a significant competitive edge.
If you want to future-proof your search presence and see your brand consistently appear in AI-generated answers, you need a strategy that’s built for both search engines and LLMs.
I help marketing agencies and small to medium-sized businesses design and execute SEO for LLM strategies that boost visibility, build authority, and drive measurable results—without the guesswork.
Contact me today and let’s create content that LLMs can’t ignore.
World Class SEO Services,
Filipino Affordability.
Book a Consultation here.
FAQS about SEO for LLMs
What is LLM in SEO?
LLM stands for Large Language Model, an AI system trained on massive datasets to understand and generate human-like text. In SEO, LLMs influence how content is discovered, cited, and presented in AI-powered search results. Optimizing for LLMs means creating content that these systems can easily understand, extract, and reference.
How to use LLM in SEO?
You can use LLMs in SEO by analyzing AI-generated search results, identifying what types of content they prefer, and structuring your content accordingly. This involves integrating relevant entities, using conversational keywords, and ensuring your information is accurate, up-to-date, and easy for AI to cite.
Is SEO possible with AI?
Yes. AI not only supports SEO but is now a major driver of it. AI tools can help with keyword research, content generation, competitive analysis, and optimization. However, ranking in AI-generated answers requires additional strategies, like entity optimization and multi-platform content presence.
Can LLM do optimization?
An LLM can generate and recommend content improvements based on patterns in its training data. While it can’t directly update your site, it can provide suggestions for keyword targeting, structure, and clarity—helping you fine-tune your SEO strategy.
How do you measure LLM search visibility?
Track your LLM visibility by monitoring brand mentions in AI-generated answers, impressions for entity-related queries in Google Search Console, and changes in branded search volume. Tools that track AI answer citations can also help you measure performance beyond traditional rankings and clicks.
Related SEO Posts
SEO Content Strategy: What Does it Take to Rank and Convert
Key Takeaways Content without strategy does not scale. Well-written articles alone will not rank consistently. Search engines reward structured topic coverage, internal linking, and documented planning that builds topical authority over time. Search intent...
Google AI Mode SEO Impact: What Every Business Needs to Know in 2026
Key Takeaways Google AI Mode is accelerating zero-click search. With up to 93% of AI Mode sessions resulting in no website visit, ranking alone is no longer enough to drive traffic. Visibility now depends on citations, not just rankings. If your brand isn’t...




